Ancient Egyptian Houses: Symbols of Warmth and Social Power
Ancient Egyptian houses are a representation of the early Egyptians' engineering skills and how they lived in the past.
Homes, as symbols of warmth and love, are always the center of families everywhere in the world. You can now distinguish the ingenuity of Egyptian houses in antiquity and their designs.
You might imagine great palaces and elegant halls when you think of the pharaoh’s wealth and power. However, how did the Egyptians truly live? Did they all live in elegant houses, given their vast land power? Their houses were not just structures but a representation of a flourishing and incomparable culture that emerged in the past.
Describing Ancient Egyptian Houses
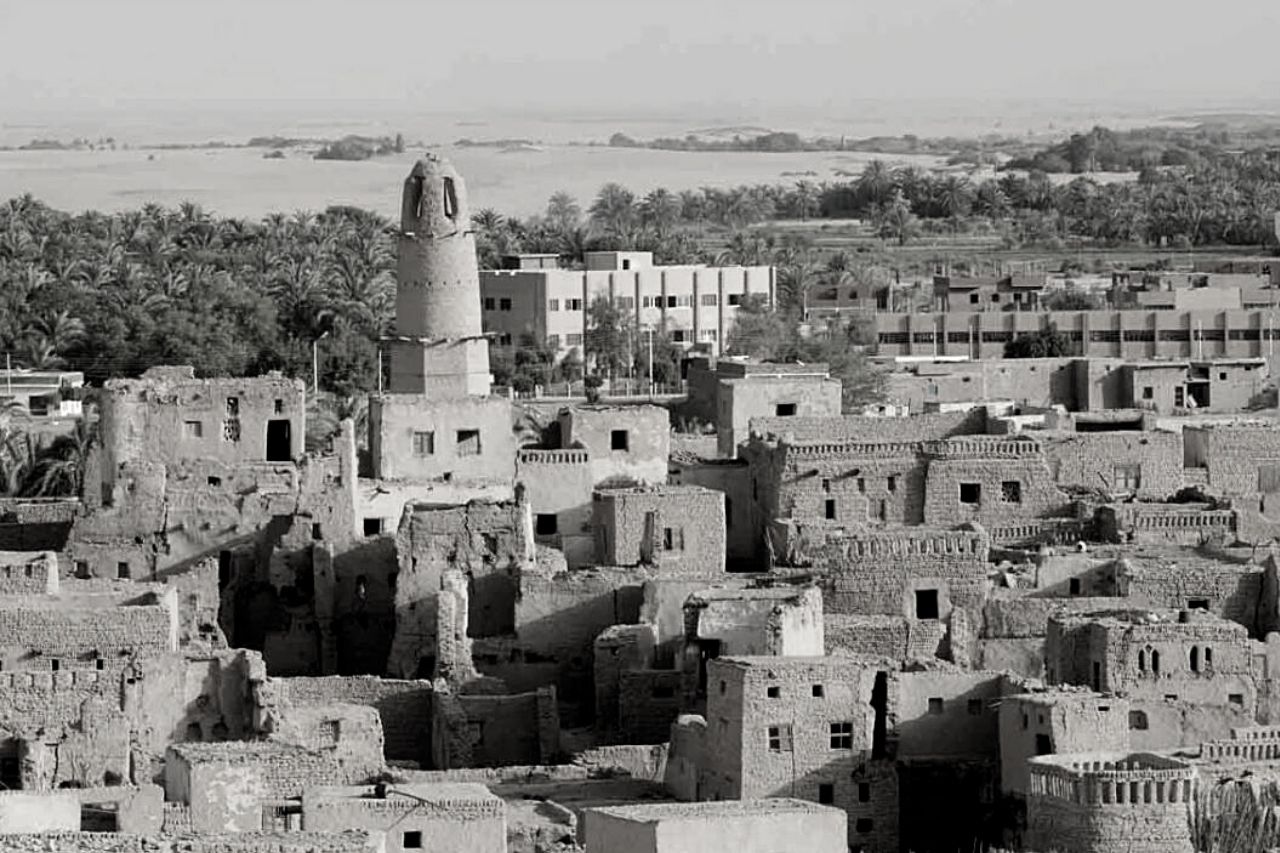
Interestingly, Egyptians in the past built homes from bricks, which were carefully made of dried mud and papyrus. They were so innovative that they invented molds to produce bricks. These were not just ordinary bricks because they were combined with straw or dried papyrus for strength and durability.
Considering a large part of Egypt is predominantly desert, it was understandable to know that wood was scarce. They only had limited use of wood for windows or doors because finding sources of wood in Egypt was difficult.
Large homes at that time were constructed with stones having precision and strength because they anticipated the annual flood caused by the overflowing of the Nile. However, this flooding was also beneficial for them because it was the perfect time to obtain an abundant supply of mud that they would mold into bricks.
Without much explanation, you could understand that everything happening in Egypt was meant for a reason and that they were talented enough to recreate or reuse something to satisfy their needs. A classic example was the danger of the flood that produced more mud for ancient Egyptian housing. It was kind of devastating, but it was a chance for them to gather mud for brickmaking.
Do you know that brickmakers in the past would gather mud and straw and then add water to form bricks? It was not easy and simple because they had to mix them well and smash them with their feet to achieve the proper strength and consistency needed for bricks.
The mixture would then be placed in a mold, shaped like bricks, and dried in the sun. You might think that this process is easy, but only experienced brickmakers could produce the exact strength and texture of this material. They had to test its accuracy before it was set for construction.
Careful enough, brickmakers made sure to mold bricks that would pass the test of time. Thanks to ancient Egyptian engineering and architectural knowledge, some of their structures built hundreds of years ago are still standing with pride to show how Egypt commanded the world in the past.
Various Houses Based on Social Status
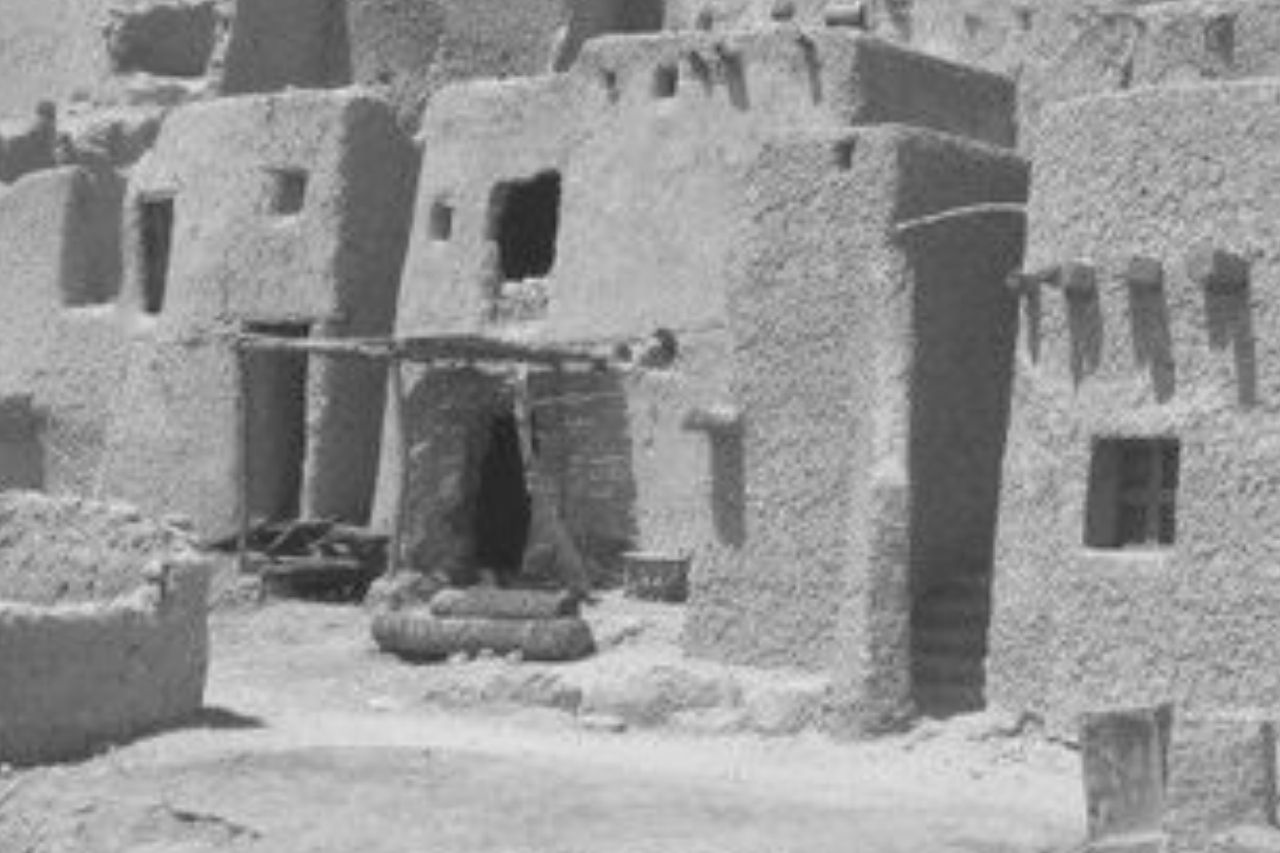
Homes in ancient Egypt were built based on the owner’s social status. For instance, farmers lived in modestly designed houses with limited pieces of furniture. These houses would normally contain beds, stools, and tables.
Simplicity was encouraged because they knew that once flooding occurred, they could only save their lives instead of their properties.
Craftsmen built one- or two-story houses with flat roofs and made of mud bricks for their families. These houses were more colorful than those of peasants because their walls and roofs were covered with tiles and were already painted.
Because the craftsmen knew how to build, their houses were made with better quality and design. Their homes included a reception room, a living room, and bedrooms. They also had a cellar as a storeroom for their food and drinks.
They built an extension outside for the kitchen strategically planned with a mud-brick oven. Those houses allowed you to go upstairs through the stairs placed on the exterior of the house.
Affluent people, such as nobles, government officers, doctors, and lawyers, made ancient Egypt shelters with larger and sophisticated designs. They were picky considering they had more wealth to produce a luxurious abode.
Thus, included in their house designs were palatial reception halls and living rooms, which were highlighted with an open garden, a fishpond, and ornamental plants. Aside from the large discrepancy in the sizes of these houses, the haves and the have nots typically had a wide gap in terms of lifestyle.
You would find it attractive to stay in their bedrooms because they had their own bathrooms inside. Their interior designs were more natural and charming, and the entire house was adorned with expensive beds, chairs, intricately designed furniture, vases, and painted clay pots.
Disadvantages of Brick Houses
You have learned that those people in the lower part of the society lived in humble houses, whereas the house designs became more elegant for those who belonged to the more elite social status. What are the disadvantages of brick houses? Could they survive natural disasters?
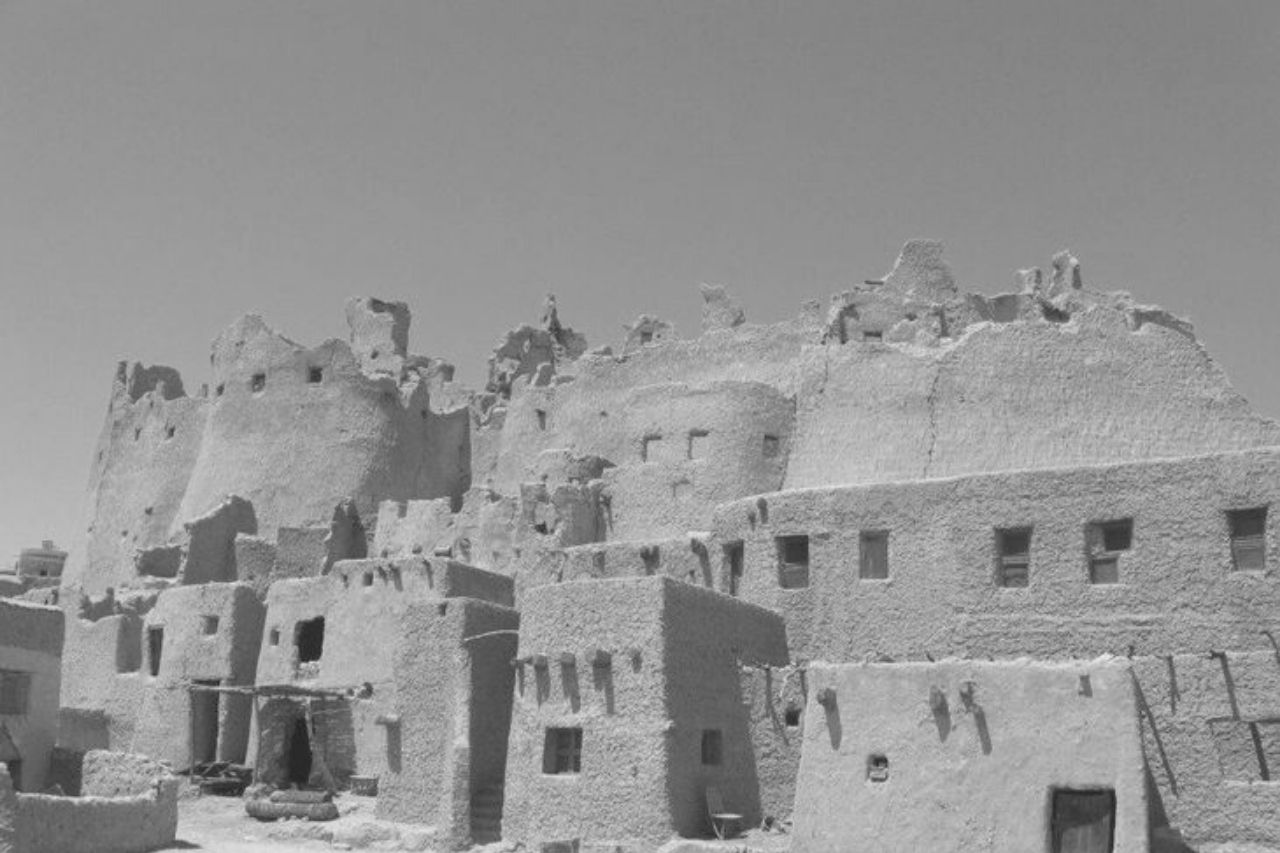
Egyptian houses in the past were basically made of dried bricks with materials that could not withstand years of exposure to the elements from the effects of flooding and the strong winds from the desert.
They weakened fast, such that Egyptians perennially repaired or rebuilt their houses after a few years of construction. Pests, such as rats, also caused damage to ancient houses. Rats loved to dig holes in the mud bricks because they were made of mud and would be easy to burrow into.
Residences of Pharaohs
Deserving of affluence and a regal life, the royal family resided in well-planned residential palaces made of stone, marble, and high-quality materials imported from other countries. You would see that their residences befitted the classical lifestyle of the pharaoh and his family.
They comprised imposing halls worthy of the highest ruler in the country. With the Egyptians’ superb knowledge in structural designs, palaces were built with a magnificent size, plan, and materials and elaborate designs beyond any palaces known in the land at that time.
How Did They Build Royal Palaces?
Royal palaces were built with two gigantic sections: the hall that would answer the needs of the pharaoh and the other section for his royal business and the throne.
Palaces were built rectangular with massive towers to show the immense wealth of the king. The towers commanded honor and respect and were decorated with crown pillars. Reconstructions were held to improve the royal splendor of the kingdom, so palaces had been redesigned into a palace–temple complex.
More Innovations in the Palace
Various pharaohs had different tastes when it came to their abode, such that constant developments in the palaces had been made to fit the requirements of the royal residents. You can imagine how grandiose the palaces were when they were designed with huge courts, colossal pillars, and gigantic halls. There were private rooms for the king’s family, and outside were glamorous gardens, lakes, and monumental pillars.
A great example of affluence was the palace–temple of Ramses III, who reigned in the Twentieth Dynasty around 1150 BC. It included the royal palace, elegant temples, magnificent towers, and sophisticated houses for the royal family members.
They were assured of total protection inside the royal residence, where the family members enjoyed the comfort, warmth, and elegance of their abode.
You know that the pharaoh’s family needed strict security, such that palaces were usually built like a complex of houses and halls to secure the privacy of the royals.
They were able to establish a feat of engineering in the temples and palaces during that time. It is a pity that we can’t see all those palaces as they have all vanished.
Nonetheless, remnants of the palace of Ramses II, known as Ramses the Great (1279–1213 BC), are still found in the country. You must notice that the standard of Egypt’s power is the magnificence of their buildings. For this matter, Ramses II made the most affluent towers of all.
Conclusion
Homes in ancient Egypt were a symbol of their social status. Egyptian brickmakers were able to build durable houses, practically made up of dried bricks and papyrus, which served as protection for their families. These houses were the very place where the Egyptians shared time with their family members and welcomed guests for a typical meeting or a grand party.
Farmers’ houses were modest and perfect for their families. Because the house was small, they had more time to encounter one another in the living room, showing more warmth.
By contrast, the bigger the house of those in the higher level of the society was, the more difficult it was for the members to see one another because they were given respective rooms for their privacy.
Royal families, on the other hand, lived in a palace–temple complex, which was secured to protect the pharaoh’s family from intruders. It was presented as majestic and dignified with colossal pillars, grand towers, and splendid halls. Carrying out the glory of their culture, palaces served as witnesses to Egypt’s escalating power in the past.
In retrospect, ancient Egyptian houses were made to represent warmth and social power. With their sophistication, the Egyptians commanded recognition.