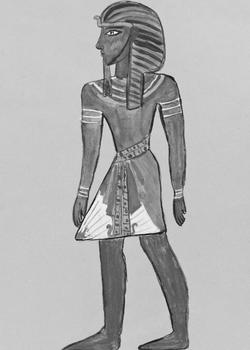
What Did Pharaoh Wear: Royal Fashion in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egyptian fashion continues to inspire today, and the pharaohs' clothes were some of the most extravagant.
So what did the Egyptian leaders wear?
We compiled this crash course guide on royal fashion and its meanings. Read on to learn more about their ancient attire.
What Did Pharaoh Wear: Fundamentals of Egyptian Fashion
Ancient Egyptian pharaohs' clothing often served symbolic purposes, but much of it was like the rest of Egyptian clothing. Egyptians wore light, breezy garments made of linen because of the hot and dry climate. Pharaohs wore linen clothing too, but the pharaoh’s dress was more exquisite and well-adorned than everyone else’s.
The following are unique Egyptian clothing items that were not reserved solely for pharaohs but were made more elaborate for the Egyptian rulers:
Shent: A wrapped skirt, typically made of linen, worn by all classes of ancient Egyptian society. Pharaohs, along with wealthy nobles and other royal family members, sometimes wore a shent of finer quality with an ornamental belt or apron.
Wigs: Many ancient Egyptians, both men and women, shaved their heads. Usually, a shaved head symbolized status, and there are many other theories, from rituals to cleanliness standards, on why an average Egyptian may have done this. What we know for sure is that wigs were trendy for keeping shaved heads covered in ancient Egypt, especially during occasions.
Khat: A simple cloth headdress made of linen worn by nobility and pharaohs. Unlike the nemes headdress (see below), a khat was never pleated or patterned and was not tied in the back.
Jewelry
Ancient Egyptian Jewelry
Ancient Egypt’s jewelry is world-renowned and among the most elegant pieces of pharaoh attire. Wealthy Egyptians wore jewelry that we are familiar with today, but some pieces had distinct elements that are now less common.
Listed below are some of the unique jewelry pieces commonly worn by the pharaohs:
Usekh: a broad collar necklace draped over the neck and shoulders, often secured with a clasp in the back. Many usekh collars were made with glazed ceramic beads and precious gemstones. Sometimes, they were made entirely from precious metals such as gold and silver.
Pectoral: a pendant or ornament worn as a brooch or attached to a necklace. The pendants often had iconography carved or painted on them and had symbolic importance.
Belts and Decorated Aprons: You might not think about belts or aprons as particularly ornate, or even as jewelry at all. But the ancient Egyptians decorated their belts and aprons with beads, gems, leatherwork, and woven details to accessorize their basic linen clothing.
Other typical jewelry included bracelets, anklets, and armlets for the limbs. Egyptians were also fond of wearing jewelry on their heads such as earrings, single amulets, and headbands called diadems.
Types of Textiles
Linen was the most common and abundant textile, but not the only one used for ancient Egyptian clothing for pharaohs. Pharaohs and wealthier upper-class individuals got away with wearing materials that were considered taboo, such as wool and leather.
The rulers were known to wear animal skins and pelts, usually of lions and leopards, to represent their rank in the Egyptian social hierarchy.
Headwear and the Many Crowns of the Pharaohs
An essential piece of the Egypt kings’ clothing was the unique collection of various crowns and head coverings strictly reserved for the pharaoh. Some head coverings symbolized the status and power of the pharaoh, while others had a specific purpose.
Listed below are these head coverings and the symbolism attached to them:
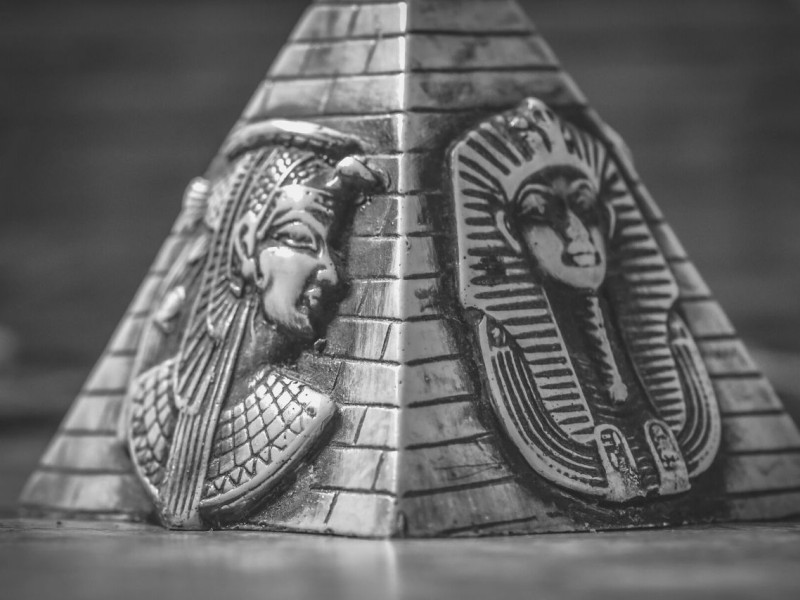
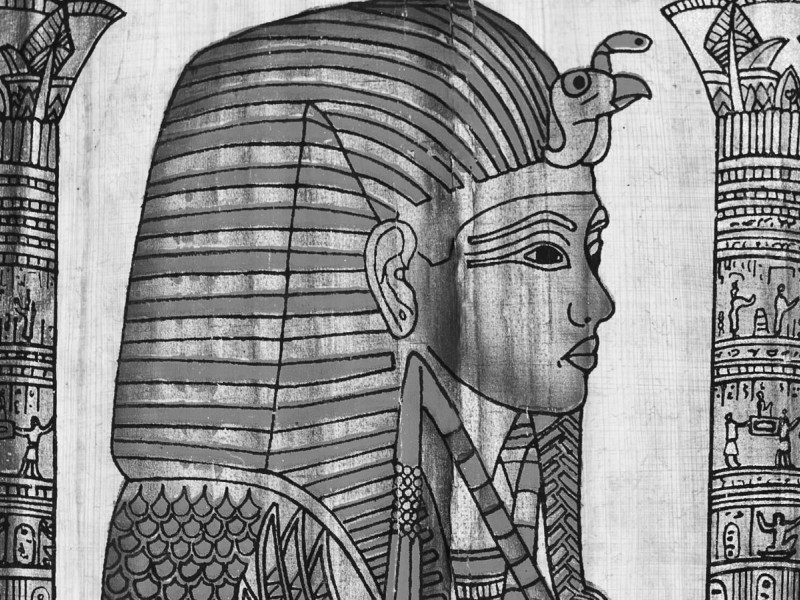
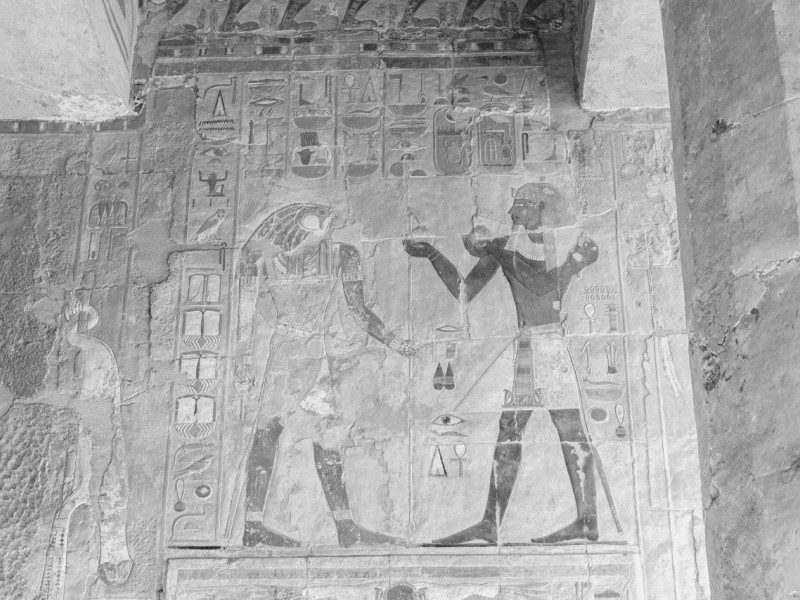
Nemes: a nemes is a head covering made of stiff cloth that is pleated and striped. It has two decorative flaps called lappets, which hang on either side of the head behind the ears and over the shoulders. The remaining cloth was gathered and tied into a ponytail in the back, symbolizing a lion’s tail. A rearing cobra and Egyptian vulture were often attached to the front.
Deshret: the Red Crown, associated with the rulership of Lower (northern) Egypt. This crown features the rearing cobra fixed on the front.
Hedjet: the White Crown, associated with the rulership of Upper (southern) Egypt. This crown features an Egyptian vulture fixed on the front.
Pschent: the Double Crown, associated with the rulership of both Upper and Lower Egypt together. Made by combining the red and the white crowns, this crown symbolized the unification of all Egypt.
Khepresh: the Blue Crown or the War Crown. Pharaohs of the New Kingdom (1550 BCE to 1077 BCE) are depicted in reliefs wearing this crown when at war. The khepresh symbolized military power and included the rearing cobra on the front.
Atef: a hedjet crown with feathers attached to either side. The atef was known as the god Osiris’ crown, and Pharaohs wore this crown because they believed they would become a form of Osiris after death.
Hemhemet: a more elaborate form of the atef crown. These often included spiraled sheep's horns and more than one rearing cobra. Pharaohs only wore this on special occasions, possibly because it was large and cumbersome.
Crowns of the Queens
Female pharaohs could wear all of the crowns that male pharaohs did, but they also had their unique crowns:
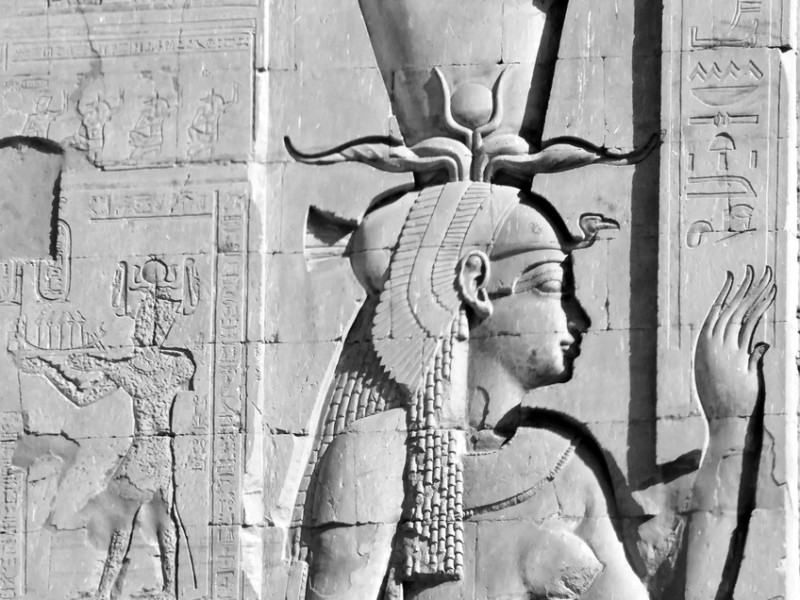
Modius: a flat crown worn by queens. The famous Bust of Nefertiti depicts the queen and wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten wearing a modius crown. It often had a rearing cobra attached to the front.
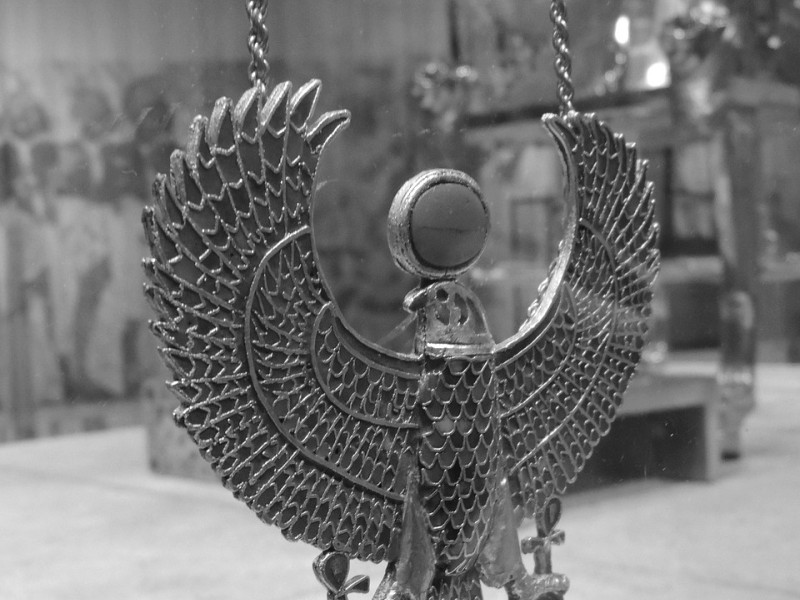
The Royal Vulture: also known as the Eagle or Falcon crown. The Royal Vulture was a headdress worn by royal wives and female pharaohs. It is shaped like a bird of prey with two wings framing the face. Sometimes, a rearing cobra was also attached to the front.
Crown Attachments
In the lists above, we mentioned two crown attachments, the rearing cobra and the Egyptian vulture.
Both accessories were symbols of power:
Uraeus: the rearing cobra. The pharaohs wore the rearing cobra to represent sovereignty, royalty, and divine authority. It also symbolized divine protection over the pharaoh and was attached to crowns, the nemes headdress, and sometimes to a headband that was worn over a wig.
Egyptian vulture: also known as the pharaoh’s chicken. The Egyptian vulture on a crown symbolized divine protection over the wearer. In general, the vulture symbolized purity, motherhood, death and rebirth.
Which Materials Did the Egyptians Use to Make A Pharaoh’s Crown?
Unfortunately, we’re not sure which materials were used to make the many crowns of the pharaohs. Archaeologists have never found a surviving Egyptian crown nor nemes. What we know about the material composition comes from surviving statues, hieroglyphs, and relief carvings.
Scholars speculate that some crowns, like the hedjet crown, were made from molded leather and decorated metallic details. Other possibilities include felt or other fabric, or they might be woven from flax straw like the deshret crown.
The Postiche
Egyptian pharaohs wore a quirky accessory strapped onto their chins called a postiche. A postiche is more commonly known as a false beard, and they wore this false beard instead of growing a real one.
Just like the atef crown, the postiche relates to the god Osiris. Wearing a false beard was another way the pharaohs connected themselves to the divine. Aside from representing Osiris, the false beard also expressed the Egyptian belief that the pharaoh was divine himself.
Few women became pharaohs, but we know that Queen Hatshepsut famously wore one of these false beards.
Conclusion
In summary, the Egyptian pharaohs had quite an impressive wardrobe. We covered a lot of ground on the extravagant costume of the Egyptian pharaohs, so let’s review:
Most Egyptians wore linen clothing, but members of the upper class could afford other textiles as well. Pharaohs were known to wear animal skins and pelts, often from leopards and lions.
Both Egyptian men and women shaved their heads. Various types of head coverings were popular, including wigs and khats, but some of them were only worn by the pharaoh:
Nemes headdress
The Red Crown, White Crown, and the Double Crown (Deshret, Hedjet, Pschent)
The Blue Crown, or War Crown (Khepresh)
Occasionally, the atef and hemhemet crowns for special occasions
Egyptian queens and female pharaohs wore the modius crown and the Royal Vulture. Female pharaohs also wore all the crowns that male pharaohs did.
Archaeologists have not found any surviving Egyptian crowns. We know what they looked like from other surviving evidence, and the rest is speculation.
You will usually find the uraeus (rearing cobra), an Egyptian vulture, or sometimes both attached to a crown or headdress.
Only pharaohs wore the false beard (postiche). There were only a few female pharaohs scholars are aware of, and we know that Queen Hatshepsut, for one, wore the false beard.
Each of the pharaoh’s clothing items symbolized power in a different way, and even a simple linen kilt was a reminder of his station because it was clean, new, and adorned. The more elaborate pieces in his wardrobe reminded the people of his connection to the divine, and the ancient pharaoh’s clothing also inspired centuries of fashion around the world.